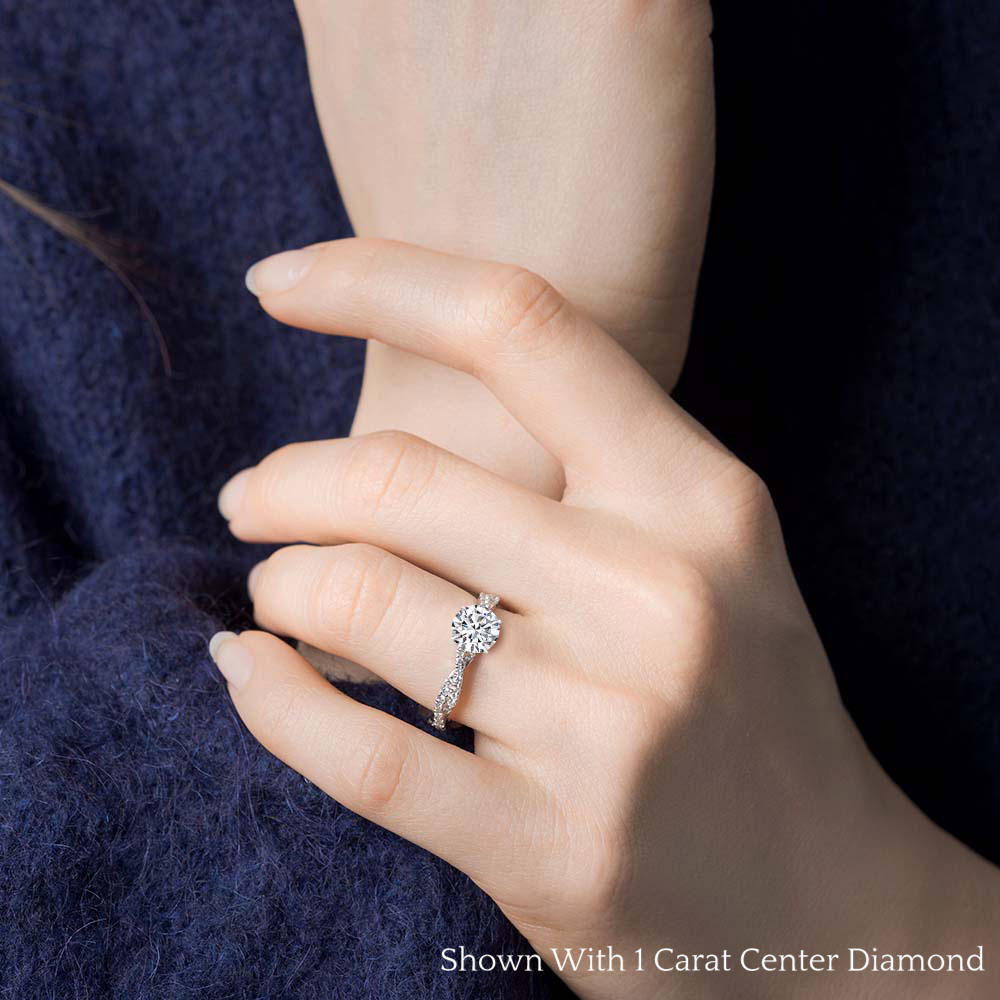
At Fascinating Diamonds® we make your diamond buying experience a pleasurable one. Our diamond education guide is exclusively designed to give you all the information that you need to properly assess any diamonds quality and value with confidence before making a purchase. Every diamond is unique, and that is the reason there’s an assortment of factors which have an effect on the price of a diamond. All you need to do is just focus on some prime aspects that would hold importance to you, and choose the diamond that would satisfy your individual standards of luxury and value. At Fascinating Diamonds®, we assist you in finding the best diamond, one that yields back the value of your money.
Diamond Grading Terminology
A diamond's cost majorly depends on its characteristics commonly known as the "4 C's". These 4C's of a diamond that are the principal descriptor and elements which mutually determine the value of a diamond are Clarity, Color, Cut, and Carat. The nearer a diamond shifts to the left of these grades on a scale the rarer and the more expensive it will be. Of all the "C's", clarity is habitually assumed to be the most important factor, but the fact is that color and cut (especially cut) have a more profound effect on the visual appearance of a diamond.
Color Of A Diamond: The Shade




Diamonds naturally come in every color of the rainbow. But what most people are concerned with is the diamonds that appear in the range of white or transparent. The best color for a diamond is no color at all or what one cannot see. They are valued by their nearness towards transparency or colorlessness – the lesser the color, higher goes their value (an exception to this case is the fancy-color diamonds, such as pinks, blues, and even some yellow ones that are highly prized and lie outside this color range). An absolutely colorless diamond allows light to pass through it quite easily, resulting in the dispersion of light as the color of a rainbow. Colors are graded from entirely colorless to light yellow. Differences from one grade of a diamond to another is quite faint, hence grading is done under restricted lighting and it takes a skilled eye many years of practice for color grading diamonds.
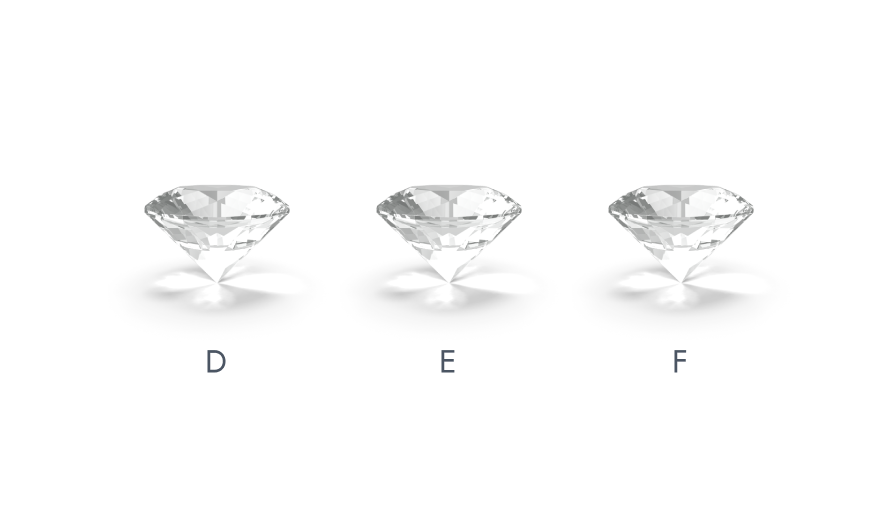
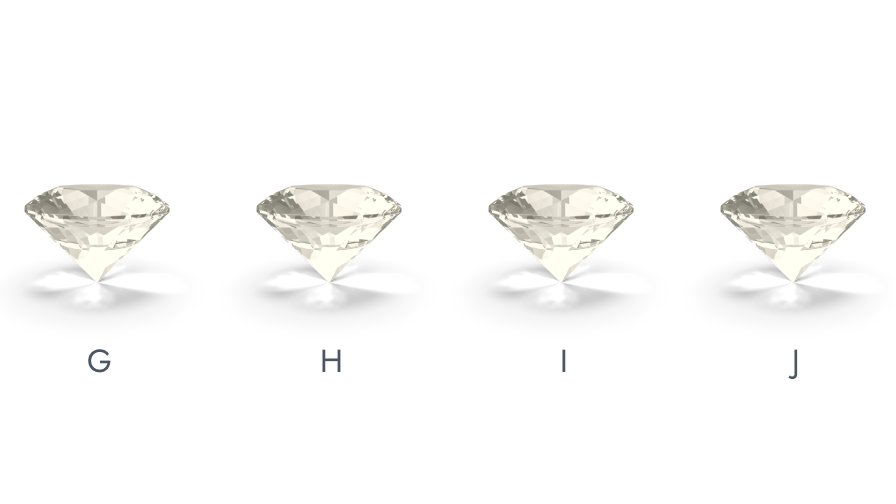
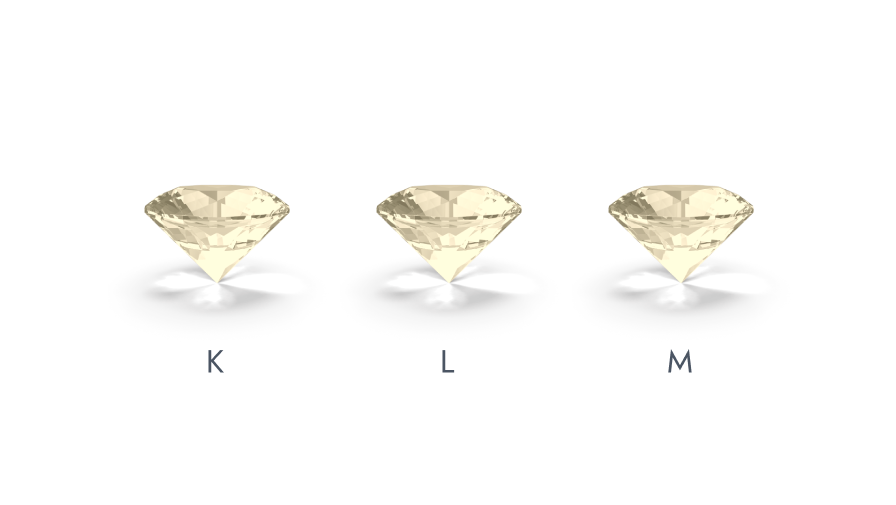
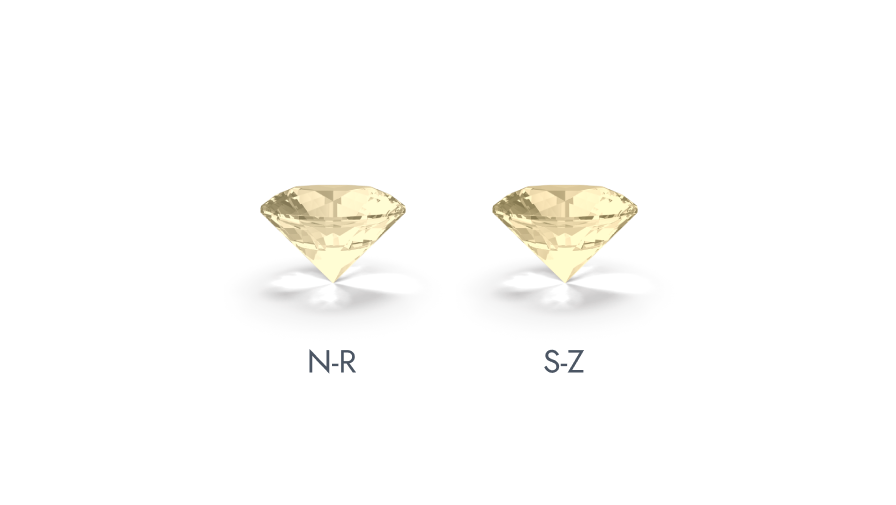
GIA’s (Gemological Institute of America's) color-grading scale for diamonds is marked as industry standard guide. The scale begins with the letter D, which signifies the whitest of diamonds or the most transparent ones and continues with escalating presence of color ranging from (light yellow to brown) to grade Z. Each letter grade has a evidently defined range of color appearance. Diamonds of recognized color are used as evaluation stones for grading. Grading is done by comparing the diamond to be graded against these "master stones" under either mock or natural light. A machine called the “Colorimeter” is also used at times for color grading but there is no substitute for a skilled human eye. Additionally, natural diamonds also found in shades of blue, green, yellow-orange, pink, red, and even black. Commonly known as 'colored fancies', these stones are exceptionally rare and precious and thus are graded according to the intensity of their color and are classified into a separate segment known as ‘Z+.
GIA Diamond Color Scale
GIA Diamond Clarity Scale

Flawless or FL :
No inclusions or blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.

Internally Flawless or IF :
No inclusions, only blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.

Very Very Slightly Included or VVS1/ VVS2 :
Inclusions are difficult to detect for a skilled grader under 10x magnification.

Very Slightly Included or VS1/ VS2 :
Inclusions are negligible and range from difficult to somewhat easy for a skilled grader to detect it under 10x magnification.

Slightly Included or SI1/SI2 :
Inclusions are obvious to a skilled grader when using 10x magnification.

Included or I1/I2/I3 :
Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification and may influence transparency and brilliance.
Carat Of A Diamond: The Weight





Diamonds are sold by carat (which is written as ct.), the unit of weight, which is perceived by many in terms of size. The word "carat" derives its name from the carob seeds that people used in olden times to counterweight their balance scales. These seeds are so homogeneous in shape and weight that even today's sophisticated instruments cannot detect more than three one-thousandths of a difference between them. Currently one carat is equivalent to 0.2 grams or 0.007 ounces (of about the weight of a paper clip). One more way of expressing the weight is by means of points. One carat is equivalent to 100 points hence a 0.25 carat diamond can well be referred to as a 25 point diamond. The size of a diamond is relative to its carat weight. Basically when a crude diamond is cut and polished it loses about 2/3 of its total carat weight.
A point which also needs to be considered is that carat weight a diamond never defines its actual shape. It is even possible to have two diamonds which have similar carat weight but have an entirely different look, which is due to the disparity in their cut and shape. Also, it is rare to find bigger rough gems of high quality in contrast to the smaller rough gems as a single 2 carat diamond can be pricier than 2 one carat diamonds of the equal quality.
It should be noted that when the carat size of a diamond increases, its price also increases at a growing rate. Bigger the diamond, progressively more rare it is. Chances are very few that one in a million mined rough stones would be large enough to produce a finished 1 carat diamond. That is the reason when the carat weight increases one has to naturally pay more not only on the whole, but on a price-per-carat basis as well. So whenever you plan to buy a perfect piece for yourself or even as a gift certain points that you need to keep in mind are the budget, taste and preference, as well as the style and setting of the ornament.
Carat of a diamond determines the weight of the diamond irrespective of the size of the diamond or appearance of the diamond. In between two diamonds of same carats, one may appear to be bigger than the other depending on the specific shape of the diamond. As for instance, a marquise cut diamond engagement ring will have the diamond appearing larger than the round cut diamond ring though may be of same carat. Depending on the carat weight of the diamond, monetary value of the diamond increases. Higher the carat weight elevated the price of the diamond because large diamonds are extensively rare and equally alluring. Although other factors like color, clarity and cut also contribute to the worth of a diamond. So, on the verge of purchasing pair of gleaming diamond earrings or any other diamond jewelry pay special importance to the cut, color and clarity also along with the carat of the diamond. The details on the carat weight of the diamond are enlisted in the description tagged along with the product information of each item. While choosing any jewelry, give preference to the 4 C’s of the diamond and select the very best jewelry that also fit the budget.
Following Scale Is Assigned As A Cut Grade By The GIA:
Excellent
Maximum fire and brilliance. Reflects almost all of the light that enters the diamond, creating excellent sparkle and life.
Very Good
Appropriately reflects most of the light that enters the diamond, producing superior fire and brilliance. In normal lighting conditions, it appears very similar to outstanding cut, at a lower price.
Good
Reflects a most of the light that enters the diamond, for an above average look. A superb value in comparison to higher cut grades.
Cut
It is the cut of a diamond that decides how much light is reflected back to the wearer, directly influencing its brilliance and fire. Diamonds are categorized into three main types of cuts:

































